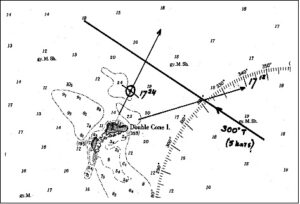
Beam and four-point bearing navigation are techniques used in piloting to determine a vessel’s position. The four-point bearing method involves taking a bearing to a landmark when it’s four points (45 degrees) off the bow, then taking another bearing when it’s abeam (90 degrees). The distance run between these two bearings is equal to the distance off when the landmark is abeam.
Four-Point Bearing Concept:
This method utilizes the principle of a right triangle where the distance run between two bearings is equal to the distance off when the object is abeam.
Procedure:
1. Identify a landmark and take a bearing when it’s four points (45 degrees) off the bow.
2. Note the distance run (or time and speed) since taking the first bearing.
3. Take another bearing when the landmark is abeam (90 degrees off the bow).
4. The distance run between the two bearings is equal to the distance off the landmark when it was abeam.
Advantages:
Simple to execute and requires only one landmark.
Disadvantages:
The distance off is only known when the object is abeam, which may be too late for taking avoiding action.
Beam Bearing Concept: A beam bearing is a bearing taken when a landmark is abeam (90 degrees to the port or starboard of the vessel’s heading).
Procedure: Take a bearing when the landmark is directly abeam.
Use: The beam bearing provides a line of position (LOP) and is used in conjunction with other bearings or fixes to determine the vessel’s position.
Combining Methods:
Both beam and four-point bearings can be used to create lines of position (LOPs).
A fix is obtained by intersecting two or more LOPs.
Important Considerations:
Compass Errors: Remember to correct compass bearings for variation and deviation (or gyro error) to obtain true bearings for plotting on the chart.
Accuracy: The accuracy of the fix depends on the accuracy of the bearings and the distance run between them.
Running Fix: The four-point bearing is a type of running fix, which relies on the accuracy of the course and distance made good between bearings.
Forrás: http://www.splashmaritime.com.au/Marops/data/text/Navtex/Navplot.htm
(Forrás: Gemini)